What Does a Catalytic Converter Do? A Complete Guide
If you own a vehicle, you've likely heard of a catalytic converter. This essential component plays a crucial role in your car's exhaust system, but many vehicle owners don't fully understand its purpose or importance. Whether you're curious about how it works, concerned about potential theft, or wondering about replacement costs, this comprehensive guide will answer all your questions about catalytic converters.
What Is a Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic converter is an emissions control device that transforms harmful pollutants from your vehicle's exhaust gases into less toxic substances before they exit through the tailpipe. Installed as part of your vehicle's exhaust system, this device has been a mandatory component in all gasoline-powered vehicles in the United States since 1975, when the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) began regulating harmful emissions.
The primary function of a catalytic converter is to reduce three specific types of emissions:
- Carbon monoxide (CO) - A toxic gas that can be lethal in high concentrations
- Hydrocarbons (HC) - Unburned fuel that contributes to smog formation
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx) - Gases that contribute to acid rain and respiratory problems
These emissions are natural byproducts of the internal combustion process that powers most vehicles. Without catalytic converters, these harmful substances would be released directly into the atmosphere, contributing significantly to air pollution and public health issues.

How Does a Catalytic Converter Work?
The operation of a catalytic converter relies on a chemical process called catalysis, where precious metals act as catalysts to facilitate chemical reactions without being consumed themselves. Here's a breakdown of how a typical catalytic converter functions:
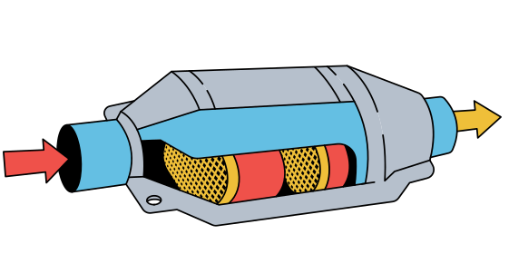
Structure and Components
Most modern vehicles use a three-way catalytic converter, which consists of:
1. Ceramic honeycomb or ceramic beads - This substrate provides a large surface area for exhaust gases to interact with the catalysts.
2. Washcoat - A rough, porous layer that increases the surface area even further and helps disperse the catalyst materials.
3. Precious metal catalysts - Typically platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals trigger the chemical reactions that convert harmful emissions.
4. Oxygen sensor - While not part of the converter itself, this component works closely with it by measuring the oxygen content in the exhaust and helping the engine's computer adjust the air-fuel ratio for optimal converter performance.
The Conversion Process
As exhaust gases flow through the catalytic converter, three main chemical reactions occur:
1. Reduction - Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are broken down into nitrogen (N₂) and oxygen (O₂) gases, which are harmless components of the air we breathe.
2. Oxidation of carbon monoxide - Carbon monoxide (CO) is combined with oxygen to form carbon dioxide (CO₂). While CO₂ is a greenhouse gas, it's far less immediately harmful than carbon monoxide.
3. Oxidation of hydrocarbons - Unburned fuel molecules (HC) are oxidized to produce carbon dioxide and water vapor.
These reactions can only occur efficiently when the catalytic converter reaches its "light-off temperature," typically around 400-600°F (204-316°C). This is why emissions are often higher when an engine is first started and hasn't warmed up yet.

Where Is the Catalytic Converter Located?
The catalytic converter is positioned in the exhaust system between the engine and the muffler. In most vehicles, it resembles a small metal canister with inlet and outlet pipes connected to the exhaust system. The exact location can vary depending on the vehicle's design:
- In front-wheel drive vehicles: Usually located under the front of the car, close to the engine
- In rear-wheel or all-wheel drive vehicles: Often positioned underneath the passenger compartment
- In vehicles with dual exhaust systems: May have two catalytic converters, one for each exhaust pipe
The converter is typically welded into the exhaust system from the factory, though some aftermarket units are designed to be bolted on for easier replacement. Its positioning makes it accessible from underneath the vehicle, which unfortunately also makes it a target for thieves who can crawl under a vehicle and quickly remove it.
Why Do People Steal Catalytic Converters?
Catalytic converter theft has become increasingly common in recent years, with police departments across the country reporting dramatic spikes in this type of crime. There are several reasons why catalytic converters have become such attractive targets for thieves:
Valuable Precious Metals
The primary reason for catalytic converter theft is the precious metals contained within:
- Platinum: Currently valued at around $900-$1,200 per ounce
- Palladium: Can be worth $1,800-$2,200 per ounce
- Rhodium: The most valuable, has reached prices as high as $20,000 per ounce in recent years
A single catalytic converter can contain 3-7 grams of platinum, 2-7 grams of palladium, and 1-2 grams of rhodium. While these amounts may seem small, the extraordinarily high value of these metals makes even these minute quantities worth the risk for thieves.
Easy to Steal (Until Now)
Catalytic converter theft is unfortunately quick and relatively simple:
- Thieves can remove a converter in under two minutes with basic tools like a battery-powered saw or cutting torch
- The external location underneath vehicles makes access straightforward
- Many parking situations leave the underside of vehicles exposed
- The crime can be committed with minimal noise, especially when using a battery-powered saw

Protect Your Investment with Our Catalytic Converter Shields
While catalytic converters have traditionally been easy targets for thieves, our specially designed shields and covers provide a robust solution to this growing problem. Our products create a physical barrier that significantly increases the time and effort required to steal your catalytic converter, deterring opportunistic thieves who rely on quick access.
Our shields are:
- Made from high-grade, tamper-resistant materials that resist cutting tools
- Custom-designed to fit your specific vehicle make and model
- Quick to install, either by yourself or at your local garage
- Cost-effective compared to the expense of replacing a stolen converter
- Designed to maintain proper heat dissipation without affecting vehicle performance
Many of our customers have reported that their vehicles were left untouched while nearby unprotected vehicles had their converters stolen. For a fraction of the cost of a replacement converter, you can gain peace of mind knowing your vehicle is protected.
Difficult to Trace
Once stolen, catalytic converters are difficult to track and recover:
- They lack serial numbers or identifying marks linking them to specific vehicles
- Scrap metal dealers and recyclers may not be required to verify the source of converters
- The black market for these parts is well-established
How Much Are Catalytic Converters Worth?
The value of catalytic converters varies significantly based on several factors:
Scrap Value
When sold for scrap, catalytic converters typically bring:
- Standard converters: $50-$250
- Higher-end converters: $300-$500
- Converters from hybrid vehicles: $800-$1,500 (hybrid vehicles like the Toyota Prius have converters with higher concentrations of precious metals)
These values fluctuate with the market prices of the precious metals they contain.

Factors Affecting Value
Several elements influence how much a specific catalytic converter is worth:
- Vehicle make and model - Luxury vehicles and certain hybrids have converters with higher precious metal content
- Size and type - Larger converters generally contain more valuable materials
- Age and condition - Newer converters typically have more recoverable metals
- Current market prices - The value of platinum, palladium, and rhodium fluctuates based on global supply and demand
It's important to note that selling used catalytic converters is legal for vehicle owners who are legitimately replacing their own converters. However, many states have enacted or are considering legislation to regulate the sale of used catalytic converters to combat theft.
How Much Does It Cost to Replace a Catalytic Converter?
If your catalytic converter fails or is stolen, replacement costs can be substantial:
Parts and Labor
The total cost to replace a catalytic converter typically ranges from $1,000 to $3,000, with luxury vehicles on the higher end of the spectrum. This price breaks down into:
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) converter: $500-$2,500
- Aftermarket converter: $200-$800 (though these may not meet emissions standards in all states)
- Labor costs: $150-$300 for installation

Additional Expenses
Beyond the basic replacement, you may encounter additional costs:
- Exhaust system damage: If thieves cut out the converter, they often damage surrounding pipes that will need repair
- Oxygen sensors: These may need replacement if damaged during theft or if they're integrated with the converter
- Check engine light diagnosis: If converter failure triggered the check engine light, diagnostic fees may apply
- Emissions testing: You may need to verify your vehicle passes emissions after replacement
Insurance Coverage
Comprehensive auto insurance typically covers catalytic converter theft, but not failure due to age or wear. If your converter was stolen:
- File a police report immediately
- Contact your insurance company to report the theft
- Be prepared to pay your comprehensive deductible
- Consider anti-theft devices for future protection
If you live in an area with high rates of catalytic converter theft, it may be worth checking your insurance coverage and deductible to ensure you're adequately protected.
How to Clean a Catalytic Converter
Over time, catalytic converters can become clogged with carbon deposits, reducing their efficiency and potentially causing engine performance issues. Before considering an expensive replacement, you might try cleaning the converter:
Signs of a Clogged Converter
Indications that your catalytic converter may need cleaning include:
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Sluggish acceleration
- Engine misfiring
- Failed emissions test
- Rotten egg smell from exhaust
- Check engine light illuminated (particularly with codes P0420 or P0430)
Cleaning Methods
Several approaches exist for cleaning a catalytic converter:
1. Fuel Additives
The simplest method is using a catalytic converter cleaner additive:
- Purchase a quality catalytic converter cleaner (brands like Cataclean, Oxicat, or CRC)
- Add the product to your fuel tank according to package directions
- Drive the vehicle to allow the cleaner to work through the system
- Repeat as needed
These products work by removing carbon deposits as they pass through the exhaust system. They're most effective for minor clogs and preventative maintenance.
2. Italian Tune-Up
This somewhat controversial method involves:
- Driving your vehicle on an open road or highway
- Accelerating to higher RPMs (within legal speed limits)
- Maintaining this higher engine load for 10-15 minutes
The theory is that higher exhaust temperatures can burn off carbon deposits. While this may help with minor clogs, it won't fix serious blockages and could potentially damage other components if there's a severe clog.
3. Direct Cleaning
For more severe cases, direct cleaning may be necessary:
- Remove the catalytic converter (best done by a professional mechanic)
- Soak it in a cleaning solution like sodium hydroxide or specialized catalytic converter cleaner
- Rinse thoroughly and allow to dry completely
- Reinstall the converter
This method is typically best left to professionals as it involves handling hazardous chemicals and potentially complicated removal and reinstallation.
4. Pressure Washing
Some mechanics use this technique for severely clogged converters:
- Remove the converter
- Use a pressure washer to blast through carbon deposits
- Allow to dry completely before reinstallation
It's worth noting that cleaning methods have limitations. If your catalytic converter is damaged, melted, or has failed internally, cleaning won't resolve the issue, and replacement will be necessary.
Can You Drive Without a Catalytic Converter?
Technically, most vehicles will still run without a catalytic converter, but doing so raises several significant concerns:
Legal Issues
Driving without a catalytic converter is illegal in all 50 states and can result in:
- Fines: Penalties for removing a catalytic converter can range from $250 to over $10,000 depending on the state
- Failed inspections: Vehicles won't pass emissions testing without a functioning converter
- Registration problems: Many states require passing emissions to renew vehicle registration
Performance Effects
Removing the catalytic converter affects vehicle performance in several ways:
- Increased noise: The exhaust will be noticeably louder
- Check engine light: The oxygen sensors will detect the missing converter, triggering warning lights
- Potential performance issues: Modern engine management systems expect back pressure from the catalytic converter; its absence can cause erratic performance
- Possible ECU problems: The engine control unit may attempt to compensate for the missing converter, potentially affecting fuel economy
Environmental Impact
The environmental consequences of driving without a catalytic converter are substantial:
- A single vehicle without a functioning converter can emit as much pollution as 20-30 properly equipped vehicles
- Harmful emissions like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides increase significantly
- These pollutants contribute to smog, acid rain, and respiratory health problems
If your catalytic converter has been stolen or has failed, it's advisable to have it replaced as soon as possible. While the cost may be significant, the legal, environmental, and potential long-term vehicle complications make driving without one inadvisable.
Protecting Your Catalytic Converter
Given the rising rates of catalytic converter theft, consider these preventive measures:
- Park in secure areas - Use closed garages when possible or well-lit, high-traffic areas
- Install anti-theft devices - Catalytic converter shields, cages, or specialty clamps can deter thieves
- Etch your VIN - Having your vehicle identification number etched on the converter can help with recovery and prosecution
- Calibrate your car alarm - Some systems can be adjusted to detect vibration from sawing or jacking up the vehicle
- Check your insurance - Ensure your policy covers catalytic converter theft with a reasonable deductible

Conclusion
The catalytic converter is a vital component of your vehicle's emissions control system, transforming harmful pollutants into less toxic substances. While it's an expensive part that's unfortunately targeted by thieves, understanding its function, location, and maintenance needs can help you protect your investment and ensure your vehicle operates efficiently and legally.
Regular maintenance, including occasional cleaning if performance issues arise, can extend the life of your catalytic converter. If replacement becomes necessary, consulting with a trusted mechanic about OEM versus aftermarket options can help you make the most cost-effective choice while ensuring your vehicle meets emissions standards.
By taking preventive measures against theft and properly maintaining this essential component, you can avoid unexpected expenses while doing your part to reduce harmful vehicle emissions.

